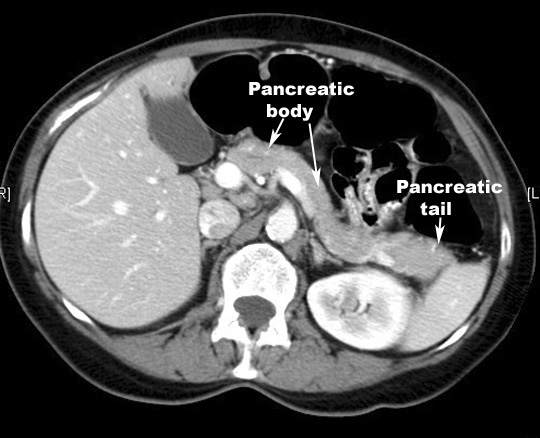
Pancreatitis
Pathology
- Pancreas is edematous and is enlarged.
- Pancreas can show acute inflammation, suppuration hemorrhage and or extensive necrosis.
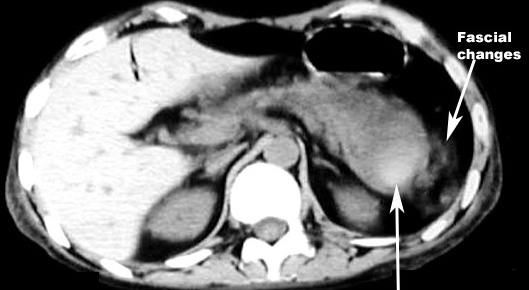
- There can be extensive peripancreatic inflammation.
- Fluid can accumulate in lesser sac and pleural space, and paracolic gutters.
- Neutrophils infiltrate the edge of the necrotic areas and extend into the adjacent lobules of fat and produce fat necrosis.
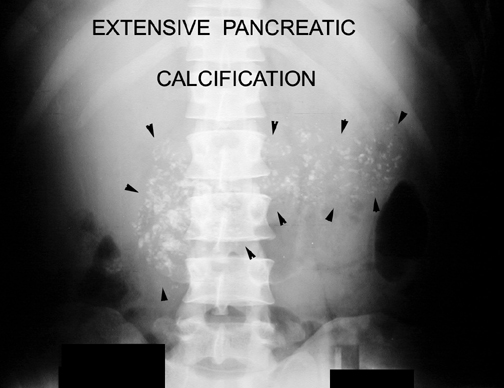
- Calcification can be seen in chronic pancreatitis.
An autopsy specimen consisting of the stomach (A), spleen (B), pancreas (D), and adjacent fat (C) reveals acute inflammation. The pancreas is swollen and hyperemic. Focal areas of green necrosis are present. Small foci of bright yellow, fat necrosis are present. The stomach is folded back so as to reveal its posterior wall and the pancreas.
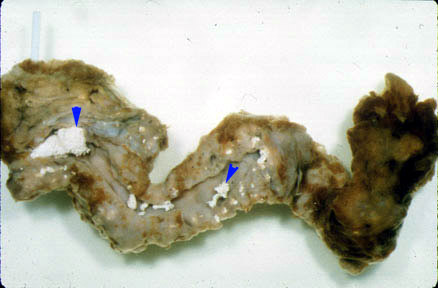
Chronic Pancreatitis
Calcification in pancreas.
Potential acute complications
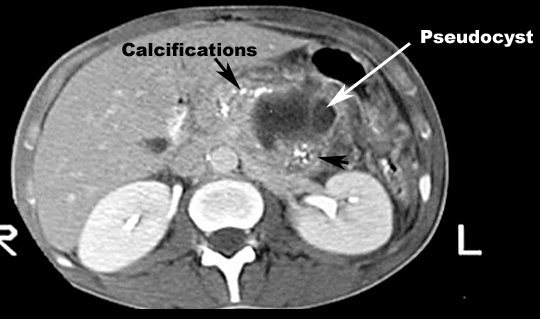
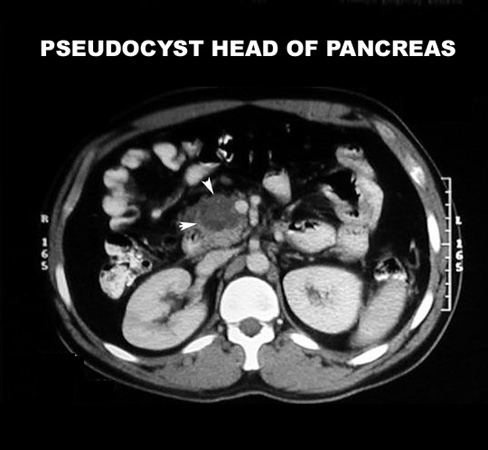
- Abscess/pseudo cyst
- As liquefaction of necrotic pancreatic tissue progresses, it will gradually take on the appearance of localized fluid collection - pseudo cyst
- This may be in the region of the pancreas or extend beyond the pancreatic region
- Pancreatic rupture/hemorrhage
- Obstructive jaundice
- Pulmonary complications in severely ill patients - ARDS
- GI obstruction
- Acute renal failure
Which is the imaging procedure of choice in a suspected case of pancreatitis?
- Plain Film
- Ultrasound
- CT scan with PO and bolus IV contrast
- If the pancreas is necrotic, CT with PO and bolus IV contrast has a sensitivity and specificity of 100 and 100%
- For drainable collections (like a large pseudo cyst), options include CT and US
- Trans abdominal ultrasound (S/S = 54/88)
- CT with PO and bolus IV contrast (S/S = 100/25)
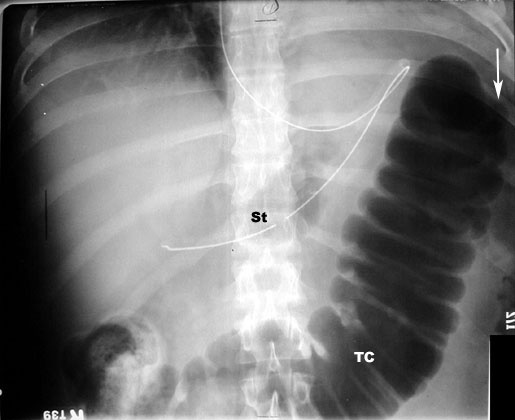
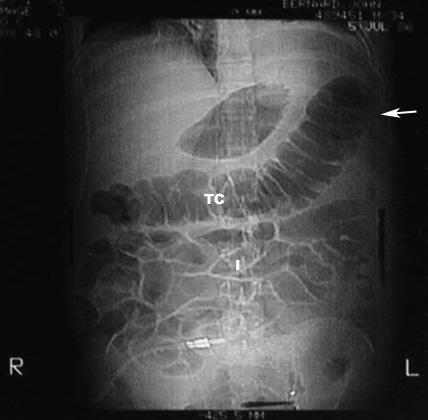
What are the anticipated imaging findings of acute pancreatitis in plain film?
- Abdominal x-ray is not diagnostic, but may show:
- Calcification in the pancreas
- Mass from a pseudo cyst
- Sentinel loop: Dilatation of duodenum
- Colon cut off: Dilated colon to the mid-transverse colon. No air seen beyond splenic flexure. This is due to extension of inflammation along mesocolon.
- Diffuse ileus ( small bowel dilatation) most commonest
- Left pleural effusion
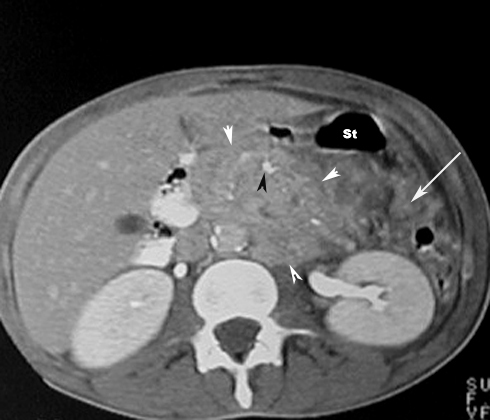
What are the anticipated imaging findings of acute pancreatitis in CT?
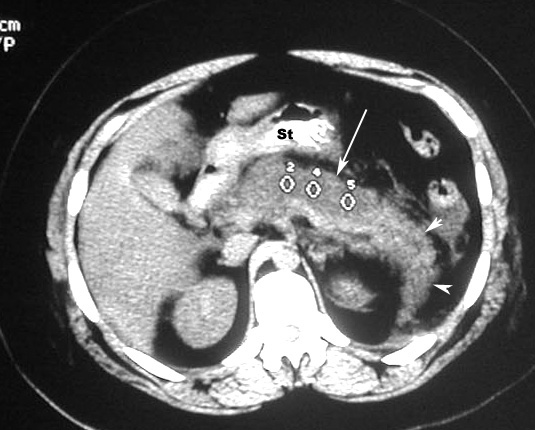
Contrast-enhanced CT of the pancreas is diagnostic and can show:- Enlargement of pancreas due to edema. Normal pancreas is about the same width as abdominal aorta. Abdominal aorta is 2.5 cm's in diameter. If the pancreas is larger than abdominal aorta, it is large. Normal pancreas, liver and spleen have similar enhancement with contrast. If pancreas is edematous it will be less dense compared to liver and spleen with IV contrast.
- Peripancreatic inflammation: linear strands in the peripancreatic fat
- Phlegmon
- Hemorrhagic: Enlarged pancreas with increased density due to hemorrhage
- Necrosis: On contrast enhanced phases the necrotic pancreatic parenchyma will show decreased or no enhancement when compared with normally enhancing viable tissue
- Fluid in the paracolic gutter
- Fluid collections: A simple peripancreatic fluid collection will not have a well-defined capsule
- Pseudo cysts: As liquefaction of necrotic pancreatic tissue progresses it will gradually take on the appearance of localized fluid collection...pseudo cyst
- Abscesses: Diffusely enlarged pancreas with air pockets
What are the imaging findings of pancreatitis in ultrasound?
- Edematous pancreas
- Gallstones
- Dilated common bile duct
- Pseudo cyst
- Due to ileus, pancreas is poorly defined in acute pancreatitis