Diverticulosis / Diverticulitis

What is diverticulosis?
- Diverticulosis refers to blind pouches leading off the alimentary tract.
- A section of colon reveals numerous diverticula which protrude from the edge of the taenia coli (*). The colon is cut in cross section revealing the diverticuli (contain feces) and the empty colonic lumen.
- Most of the time they are discovered incidentally.
- Clinical presentation changes once there is a complication.
- Inflammation (diverticulitis)
- Chronic blood loss/rarely acute hemorrhage
- Abdominal discomfort/constipation/diarrhea
What is the mode of clinical presentation of diverticulosis?
What are the potential complications of divericula?

What is diverticulitis?
- Diverticulitis is a condition that occurs when diverticula become infected and inflamed.
Acute diverticulitis occurs when a section of colon reveals acute inflammation (hyperemia, swelling) of the serosa and pericolic fat.
What are the complications of diverticulitis?
- Abscess
- Bleeding
- Fistula
- Obstruction
- Perforation
What are the imaging studies to detect findings of diverticulosis?
- Lower GI
- CT
What is the imaging procedure of choice to demonstrate diverticulitis?
- CT:
- CT is the imaging procedure of choice to evaluate diverticular disease, as it can show many aspects of disease that are not recognizable by other studies.
- For inflammation or abscess, helical CT with colonic contrast has a sensitivity and specificity of 97 and 100%.
- CT scan can assess complications better.
- Ultrasound:
- If the target diagnosis is an abscess, then ultrasound has a sensitivity and specificity of 97 and 98%.
- US can be sub optimal because of intestinal gas.
- It is operator dependent.
- Contrast enema can demonstrate divericulosis and diverticulitis, but is rarely done at present.
What are the imaging findings of diverticulitis?
- US: Abnormal wall thickening of more than 4 mm involving a segment 5 cm or longer at the point of maximal tenderness.
- CT:
- Diverticula
- Narrowed lumen
- Thickened bowel wall
- Fascial inflammatory infiltration
- Complications
- Perforation: Free air in the peritoneum
- Abscess
Image Atlas of Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis

Diverticulosis
Lower GI showing Diverticula

Diverticulosis
CT: Arrowheads point to multiple diverticula arising from the recto sigmoid. The contrast in diverticula is left over from previously administered GI contrast.

Diverticulitis
CT scan with GI contrast study showing findings of diverticulitis.
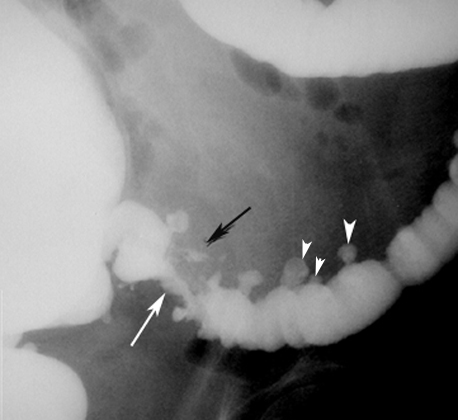
Diverticulitis with Abscess
Findings:
- White arrowheads: Diverticula
- White arrow: Narrowed lumen
- Black arrow: Perforation with intramural abscess

Perforated Diverticulum
Pneumoperitoneum
- Arrowheads point to free air.
- Arrows points to collection of fluid around bowel loops.
- Black arrows point to pericolonic fascial infiltration.

Perforated Diverticulum
Plain film